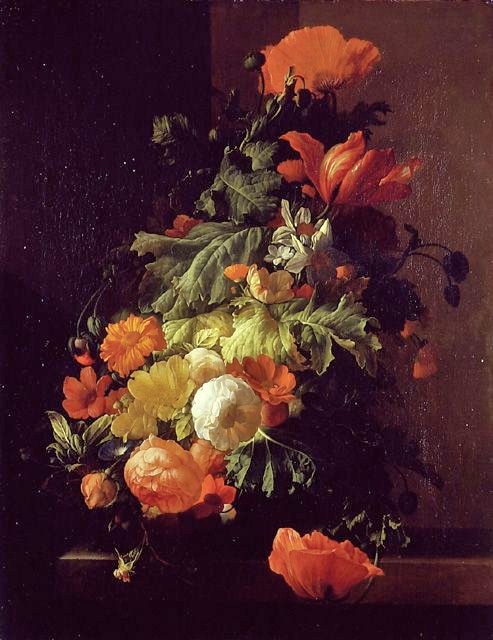.
Abraham de Lust (Flemish artist, active mid 17th century) Flower Still Life
Now an abundant everyday item, cut flowers were prized luxuries in 17th-century Europe, England, and her colonies. Only the most affluent could afford to have them in their homes and gardens. That is why early explorers of Atlantic America described the flowers growing wild in the new colonies so carefully. A general growing prosperity in Europe during the course of the 17th century, however, eventually caused flower gardens to become more popular. The garden was considered an extension of the home and vice versa, with garden bouquets often decorating the home.
Abraham Mignon (Dutch Baroque Era Painter, 1640-1679) Hanging Bouquet of Flowers
Introduced from Asia around 1600, the anemone, crocus, hyacinth and tulips were immensely popular in Europe. The Dutch trade in flower bulbs, tulips in particular, proved a highly lucrative business. In around 1630, at the height of ‘Tulip Mania,’ an exceptional tulip bulb could cost as much as an entire house on a Dutch canal.
Alexander Adriaenssen (Flemish Baroque Era painter, 1587-1661) Flowers in Glass Vase
The average citizen simply could not afford a bouquet for home. The first flower still lifes appeared in the Netherlands during the early 1600s, as a means of meeting the demand for flowers. A painting of a flower was much less expensive than an actual bouquet and lasted for generations instead of days. Many early flower still life painters were German, Dutch, and Flemish. Some trained there, then moved throughout Europe and sailed to England, as the popularity of the genre spread.
Ambrosius Bosschaert the Elder (Dutch Baroque Era Painter, 1573-1621) Glass with Four Tulips 1615
Flower still lifes were still in vogue during the 18th and 19th centuries, when the rise of large-scale commercial bulb-growing transformed the Netherlands into the flower nation that it remains to this day. Now bulbs are exported around the world.
Balthasar van der Ast (Dutch Baroque painter, 1593-94–1657) Still Life with Flowers 1632
Cornelis de Heem (Dutch Baroque Era Painter, 1631-1695) Still Life with Bird
Elias van den Broeck (Dutch Baroque painter, 1649–1708) Vase of Flowers
Jacob Marrel (Dutch Baroque Era Painter, ca.1613-1681) Flower Study
Jan Davidsz. de Heem (Dutch Baroque painter, 1606-1683-84) Still Life
Jan Philip van Thielen (Flemish Baroque painter, 1618–1667) Still Life of Flowers
Jan van Kessel (Antwerp, 1626-idem, 1679) Still Life
Maria van Oosterwyck (Oosterwijck) (Dutch Baroque painter, 1630-1693) Flower Still Life 1669
Peter Binoit (German artist, fl 1611-1620) Flowers in a Glass Beaker 1620
Roelandt Savery (Flemish Northern Renaissance painter, 1576-1639) Flowers in a Niche 1611
Simon Verelst (Dutch Baroque Era Painter, c 1644-1721) Flowers in a Vase 1669
Willem van Aelst (Dutch artist, 1627-1683) Flower Still Life 1656












+Charles+Fraser+(1782-1860)+The+Gibbes+Museum+of+Art,+Charleston,+South+Carolina..jpg) 30 May 2, 1796. Charles Fraser (1782-1860). The Carolina Art Association Gibbes Museum of Art, Charleston, South Carolina
30 May 2, 1796. Charles Fraser (1782-1860). The Carolina Art Association Gibbes Museum of Art, Charleston, South Carolina